
ABOUT THE PROJECT
DESMO-LD: Decentralized Smart Oracles for Trusted Linked Data
DESMO-LD aims to design, implement and showcase a trustful Oracle prototype to interact with the ONTOCHAIN infrastructure and to provide necessary data for the operation of its applications. In particular, the project enables Ethereum Smart Contracts to gather off-chain Linked Data sources through Decentralized Smart Oracles (e.g., iExec DOracles).
DESMO-LD exploits the results of the NGI DAPSI project DASI Breaker which provides an interoperable access to Linked Data granted by open and standard protocols/APIs like NGSI-LD, Linked Data Platform 1.0 and SOLID. With this respect, DESMO-LD brings a mutual benefit to the data portability and blockchain communities.
From VAIMEE's business perspective, DESMO-LD opens the possibility to create new opportunities in contexts where trustworthy content handling is essential, such as providing data evidence in quality and compliance audits, detecting anomalous conditions in industrial IoT or in environmental monitoring devoted to mitigating climate changes. Eventually, the business model behind the reward granted by the blockchain in terms of cryptocurrency (e.g., ETH) is at the same time very appealing and promising to enhance VAIMEE’s business.
Website: https://github.com/vaimee/desmo-ld
Motivation for the project:
DESMO-LD addresses the objectives of designing new trustful decentralized Oracles to poll semantic data from off-chain data sources. DESMO-LD introduces novel opportunities for ONTOCHAIN Ethereum Smart Contracts to cover specific needs of an ever-evolving Web of Data.
Generic use case description:
DESMO-LD would play a crucial role as a key enabler to consume web hosted knowledge graphs and ontologies. It enables the progressive ingestion of semantically enriched facts coming from heterogeneous (IoT) data sources like SOLID pods, NGSI-LD, SPARQL endpoints into the blockchain.
Essential functionalities:
DESMO-LD aims to enrich the on-chain world with off-chain Linked Data sources and to provide an efficient way to retrieve those data both in an active (i.e., subscriptions) and passive (i.e., queries) mode.
How these functionalities can be integrated within the software ecosystem:
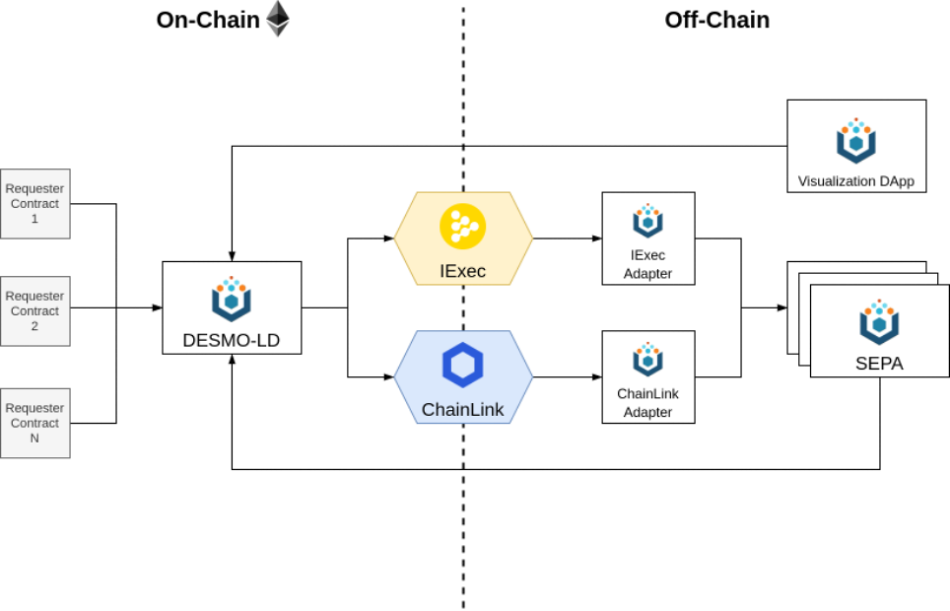
DESMO-LD is in fact a set of Smart Contracts to collect and manage Linked Data requests and subscriptions from Requester Contracts. On each request, DESMO-LD selects a set of SEPA nodes and adds them to the received request. After that, acting as a proxy, it forwards the request to ChainLink and iExec for processing.
Gap being addressed:
Within the ONTOCHAIN ecosystem, DESMO-LD aims to find a solution for: the centralization of the data source; the need for Smart Contracts to actively receive data without using polling mechanisms; seamlessly aggregate data from multiple sources; gas prices for highly volatile off-chain values.
Expected benefits achieved with the novel technology building blocks:
The availability of trustworthy and interoperable data would have a positive impact on many different domains, like providing data evidence in quality and compliance audits, detecting anomalous conditions in industrial IoT or in environmental monitoring devoted to mitigating climate changes.
Potential demonstration scenario:
Quality and compliance shall be relevant scenarios where DESMO-LD technology could make the difference in terms of scalability of data shared among the actual operators that could lead to prompt up-to-dated data from different sources.
PROJECT OUTCOMES
The DESMO-LD project aims to provide a fully integrated distributed solution for consuming IoT external data, enriched with Web of Things semantics and data model, inside the ONTOCHAIN. DESMO-LD is a distributed IoT oracle powered by the decentrilized computing platform of Iexec. Users can interact with the system with custom designed queries, tailored for IoT use cases, and collect sensor data from multiple distributed data sources.
This addresses the ONTOCHAIN call's objectives of designing new trustful decentralized Oracles to poll semantic data from off-chain data sources. Besides, DESMO-LD introduces novel strategies to solve the known interoperability problems thanks to the heavy deployment of standard ontology and semantic oriented consensus algorithms for data quality and trustworthiness.
Demo:
Repositories:
Desmo-contracts: https://github.com/vaimee/desmo-contracts
Desmo-dapp: https://github.com/vaimee/desmo-dapp
Desmo-front: https://github.com/vaimee/desmo-front
Desmo-sdk: https://github.com/vaimee/desmo-sdk
Zion: https://github.com/vaimee/zion
Documentation:
https://github.com/vaimee/desmo
More details:
Use case Scenario
Decentralised EV sharing (DEVS):
DEVs is a fully decentralised platform for electric vehicles sharing, based on blockchain and semantic technologies. Thanks to a detailed semantic description of vehicles, service providers can register their cars/scooters/bikes in the system and users can exploit them for their needs. The blockchain technology ensures a fair and trusted exchange of services thanks to Smart Contracts and IoT Oracles.
Scenario 1 - Users that want to use this service. The following steps take place when a user uses the service:
-
User is seeking a vehicle. Users can visualise the vehicles nearby.
-
The DApp will retrieve the list of vehicles and the user chooses accordingly.
-
The user stakes some tokens for reserving the vehicle for a certain amount of time.
-
The on-chain protocol unlocks the vehicle only after the payment is verified.
-
The user is allowed to reach the destination.
-
The process is concluded, and the tokens are distributed between the parties. In this final phase, penalties and bonuses are calculated and applied.
Scenario 2 - Offering Facilities. The following steps take place when a user uses the service:
-
Touristic facilities reserve a part of the community-driven fleet for their own users as an additional service included in their offering.
-
Facilities can customise fleet behaviour and management.
Scenario 3 - Suppliers that want to be part of the ecosystem. The following steps take place when a user uses the service:
-
Users/organisations can register their devices and set a fair price per hour on-chain, and they become part of the fleet.
-
If users/facilities rent their vehicles, suppliers are paid accordingly.
ONTOCHAIN partners that support the scenario
CARECHAIN: Their insurance contracts can be seen as clients of our architecture, but at the same time, the ecosystem gives them the ability to install TDDs where they can register new sensors easily. Moreover, thanks to the W3C WoT, it will be possible to have a standard and homogeneous interface for managing the different devices on the market: abstracting the numerous protocols, data formats, etc.
DKG: DESMO-LD could use its distributed storage to organize the retrieved data in order to have an “historical” archive of the most requests information. In addition to the actual data, DKG storage can be used to save the TDs of the WTs from which the data came.
REPUTABLE: DESMO-LD can take advantage of this system to model and manage the reputation of the TDD nodes that are participating in the network.
GEONTOLOGY: The output of the project can play a crucial role in DESMO-LD. Specifically, device Thing Descriptions can be augmented and tagged with proofs of offsets following the Geontology guidelines. As JSON-LD documents, TDs can import an ontology and add new terms with information about the location of the device and the corresponding proof.
Semantic content and content transfer
Semantic content that will be used by this application idea is summarised in the following points:
- Detailed description of vehicles (it would require an ontology of existing vehicle types)
-
Vehicles capabilities
-
Geospatial data
-
User identity (e.g., license)
- Reputation scoring data
TEAM
Principal Investigator, PhD (2005) and M.Sc. (2001) in Electronics, Computer Science and Telecommunication Engineering; Junior Assistant Professor of Digital Design Principles and Computer Architecture (2020-2023); co-founder and President at VAIMEE.
Technical Project Leader, PhD student (2021) and M.Sc. (2019) in Computer Science on blockchain technologies and IoT for structural health monitoring.
Project & Marketing Manager, M.BA (2011) in Innovation and Organization of Culture and the Arts.
R&D, PhD (2021) in Engineering and Information Technology for Structural and Environmental Monitoring and Risk Management; M.Sc. in Computer Engineering (2017); invited expert of the W3C Web of Things working group (2020 – now); co-founder and Vice-President at VAIMEE.
Ontology designer and Linked Data expert, B.Sc. (2021) in Biomedical Engineering; design of ontologies for Web of Things (e.g., MODBUS) .
Developer, B.Sc. (2020) in Computer Engineering; second year master student in Artificial Intelligence.
Developer, B.Sc. (2020) in Computer Engineering; second year master student in Artificial Intelligence.
Developer, M.Sc. (2019) in Artificial Intelligence Applied to Automation and Robotics, Centro Universitário FEI, São Bernardo do Campo, SP, Brazil.
ENTITIES
VAIMEE provides B2B solutions for the development of interoperable services and applications on top of an open software solution driven by Semantic Web technologies and Linked Data standards.












 This project has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 957338
This project has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 957338




